Machine learning comes under artificial intelligence and computer science. It uses a wide Machine learning comes under artificial.
intelligence and computer science. It uses a wide range of statistical and computational techniques to enable machines to improve their performance on a specific task by learning from data. In simple terms, machine learning is a process in which a computer program learns from data, without being explicitly programmed.
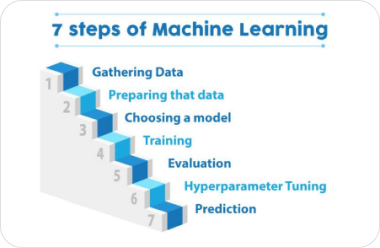
At its core, machine learning involves training a machine learning model on a dataset, which contains examples of inputs and outputs for a given task. The model then uses this dataset to learn the underlying patterns and relationships between the inputs and outputs, which enables it to make accurate predictions or decisions on new, unseen data.
There are several types of machine learning algorithms, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the correct outputs are already known. Unsupervised learning involves finding patterns or structure in unlabelled data. Reinforcement learning involves an agent learning to interact with an environment by receiving feedback in the form of rewards or punishments.
Machine learning has many practical applications in various fields, such as healthcare, finance, and e-commerce. For example, machine learning can be used to predict which patients are at a high risk of developing a certain disease, detect fraudulent transactions, or recommend products to customers based on their previous purchase history.
In summary, machine learning is a process in which a machine learning model learns from data to make accurate predictions or decisions. It involves various types of algorithms and has many practical applications in different fields. By harnessing the power of machine learning, we can automate decision-making processes, improve system performance, and make more informed decisions.